Create and Use Custom Tekton Pipelines
This use case explains how to create and use custom Tekton pipelines on the KubeRocketCI Platform. While KubeRocketCI offers pre-configured Tekton pipelines for common use cases, custom pipelines allow you to adapt workflows to meet unique project requirements. It also provides guidance on integrating and using these custom Tekton pipelines within your development processes.
Goals
- Provide a clear method for creating and configuring custom Tekton tasks and pipelines for build, review, deployment, and clean processes within KubeRocketCI.
- Offer a detailed guide on integrating custom pipelines with the KubeRocketCI platform, ensuring seamless connection and functionality.
- Clarify the process for replacing existing build, review, deployment, and clean pipelines with custom pipelines, highlighting necessary steps and considerations.
- Demonstrate the benefits of using custom Tekton pipelines in KubeRocketCI, such as improved flexibility, scalability, and efficiency in development workflows.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with this use case, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- Access to a KubeRocketCI instance with permissions to create and edit Components and Environments.
- A configured KubeRocketCI instance with at least one active Git Server (e.g., GitHub, GitLab or Bitbucket).
- Configured Argo CD instance with the Add-ons repository added.
Scenario
- Create a Tekton library in KubeRocketCI for storing and managing custom Tekton resources.
- Define custom Tekton pipelines for build, review, deployment, or clean processes based on specific project requirements.
- Integrate custom Tekton pipelines with the KubeRocketCI platform to automate build, review, and deployment workflows using Argo CD and the add-ons repository.
- Replace existing build, review, deploy, or clean pipelines with custom pipelines.
Creating a Tekton Library for Custom Pipelines
The first step in creating and using custom Tekton pipelines is to set up a Tekton library in KubeRocketCI. This library acts as a central repository for storing and managing custom Tekton tasks, pipelines, and trigger templates.
To create a Tekton library, follow these steps:
-
Open the KubeRocketCI portal. Use the Sign-In option:

-
In the top-right corner, click the three dots (⋮) menu. From the dropdown, select your profile name to access additional options:
-
Ensure that both
Default namespaceandAllowed namespacesare set to the same namespace where you want to create the Tekton library: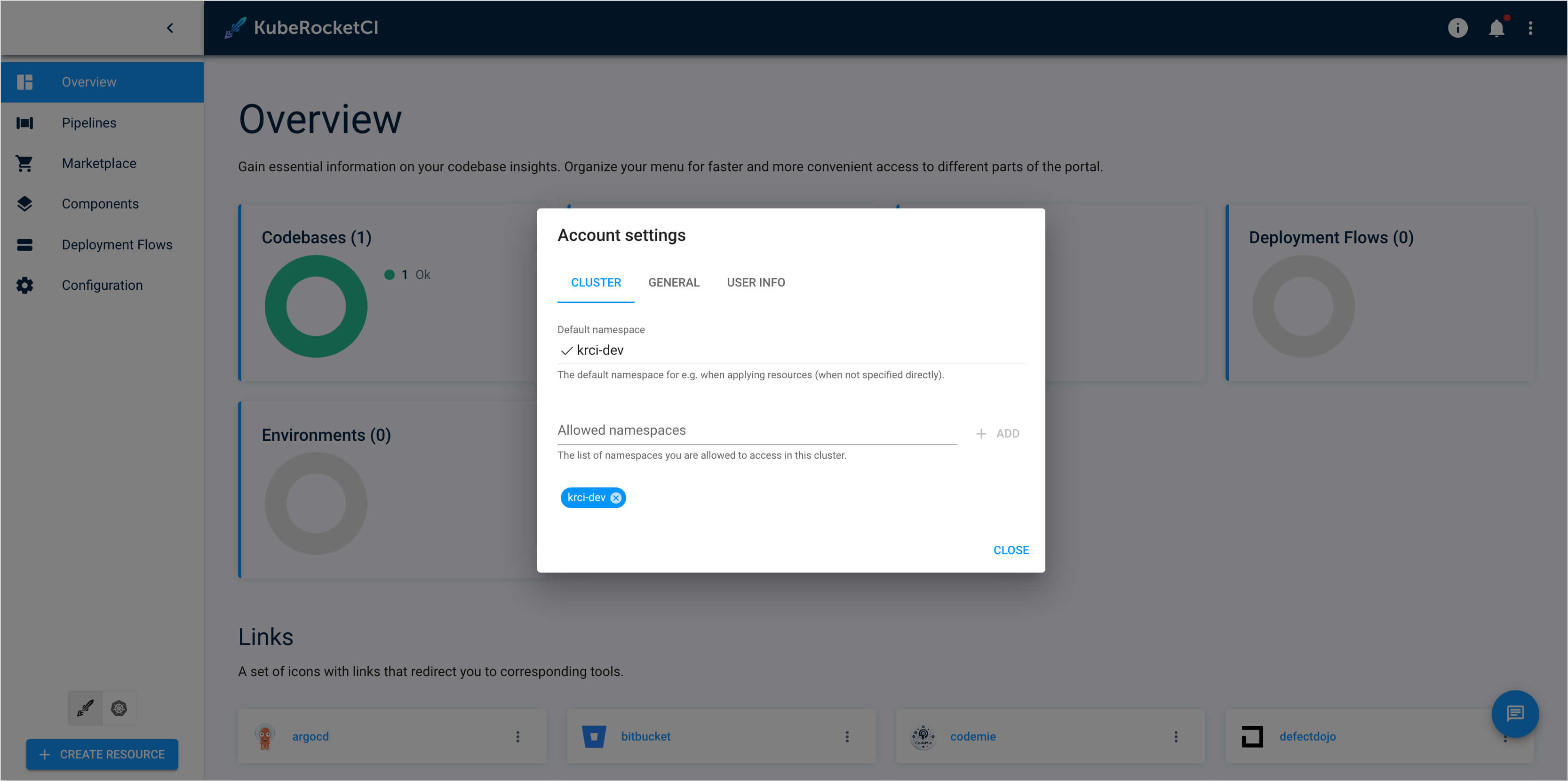
-
Click the
Componentstab in the left-hand navigation menu. Then, click theCreate Componentbutton. Choose the Component type asLibrary: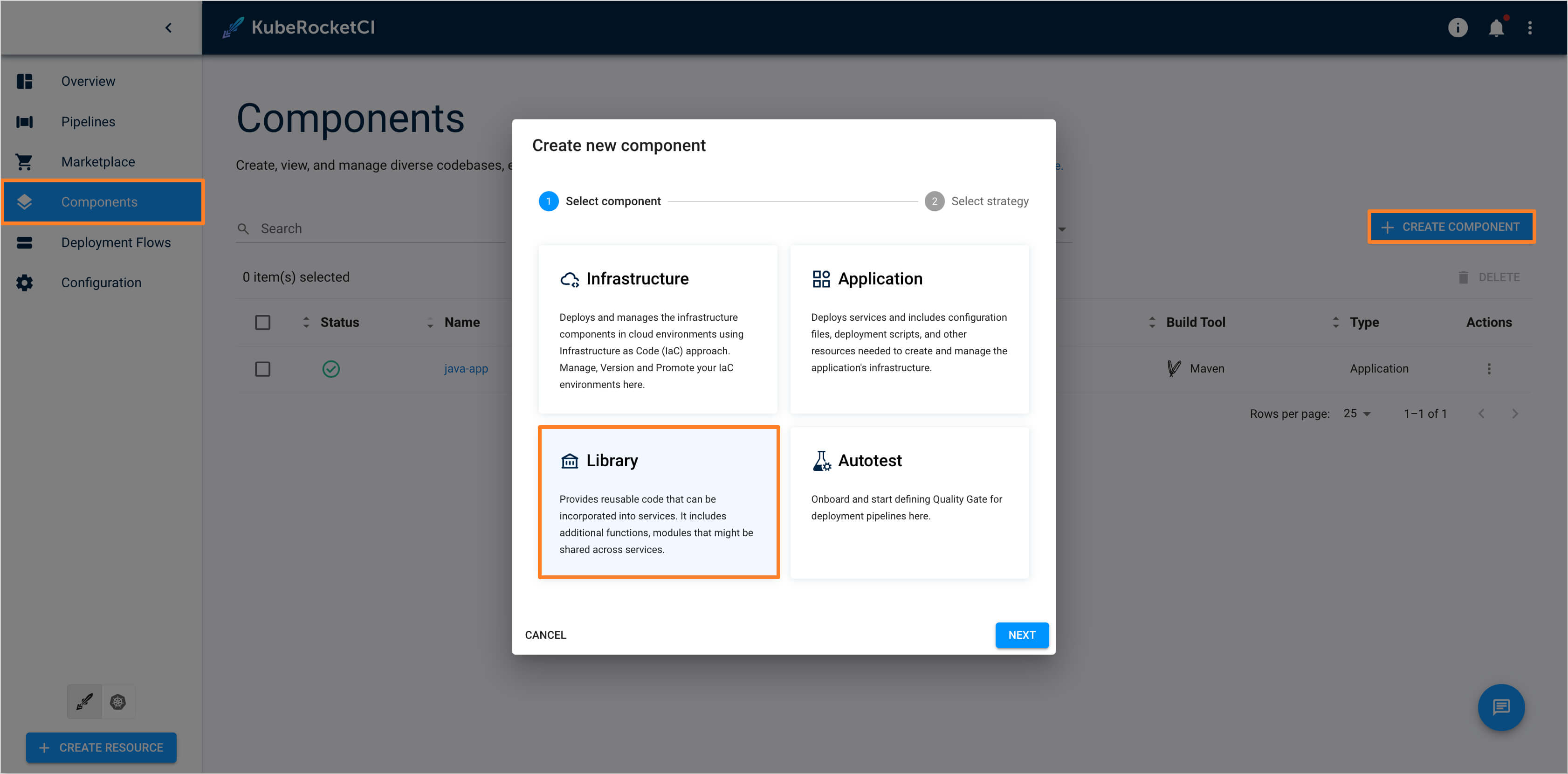
-
Select the Strategy type as
Create from template: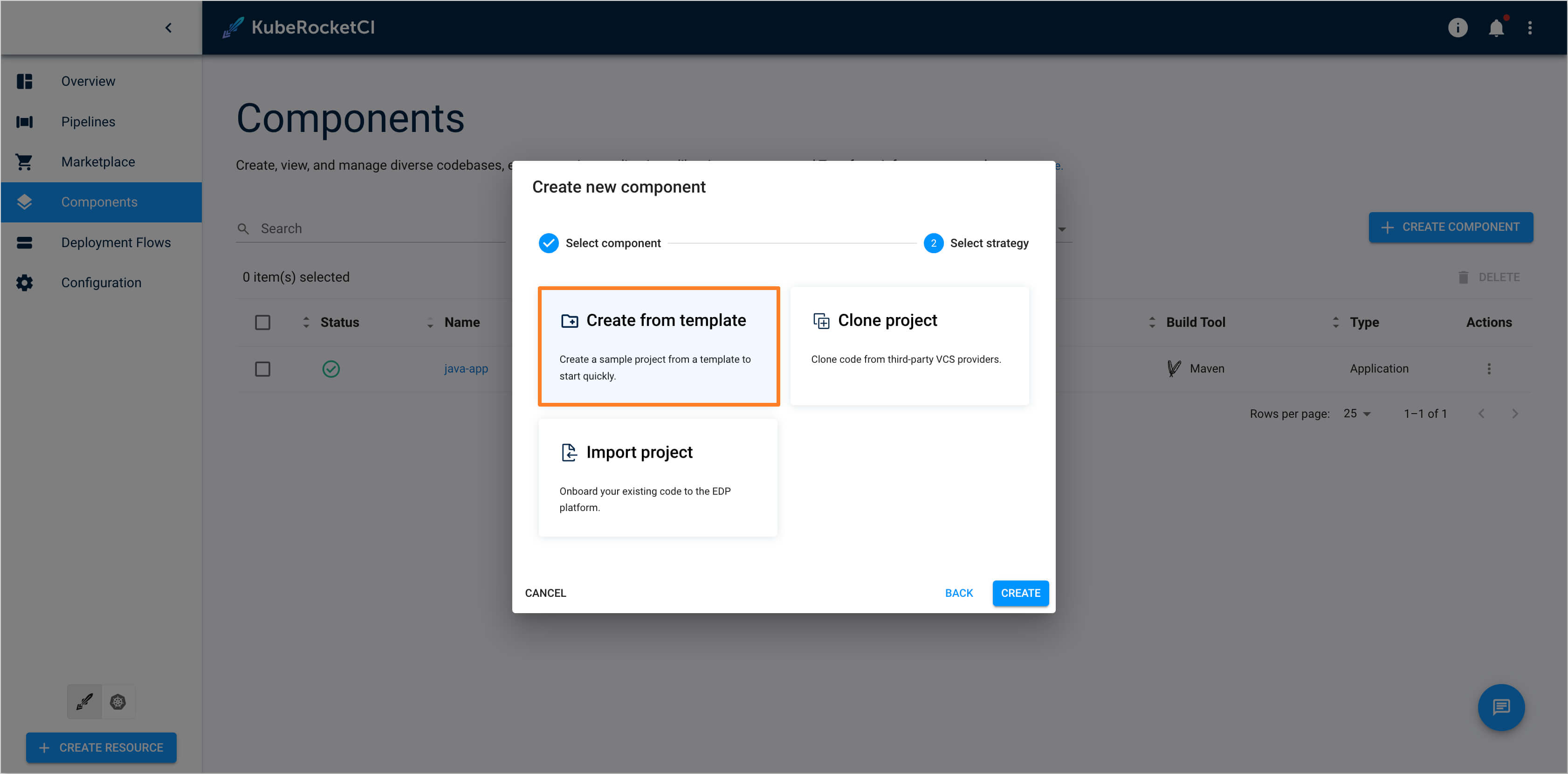
-
In the Create Library window, enter the following values:
- Repository Name:
<git-account-name>/tekton-custom-pipelines - Component name:
tekton-custom-pipelines - Description:
Repository for storing and managing custom Tekton resources - Library code language:
Helm - Language version/framework:
Pipeline - Build tool:
Helm
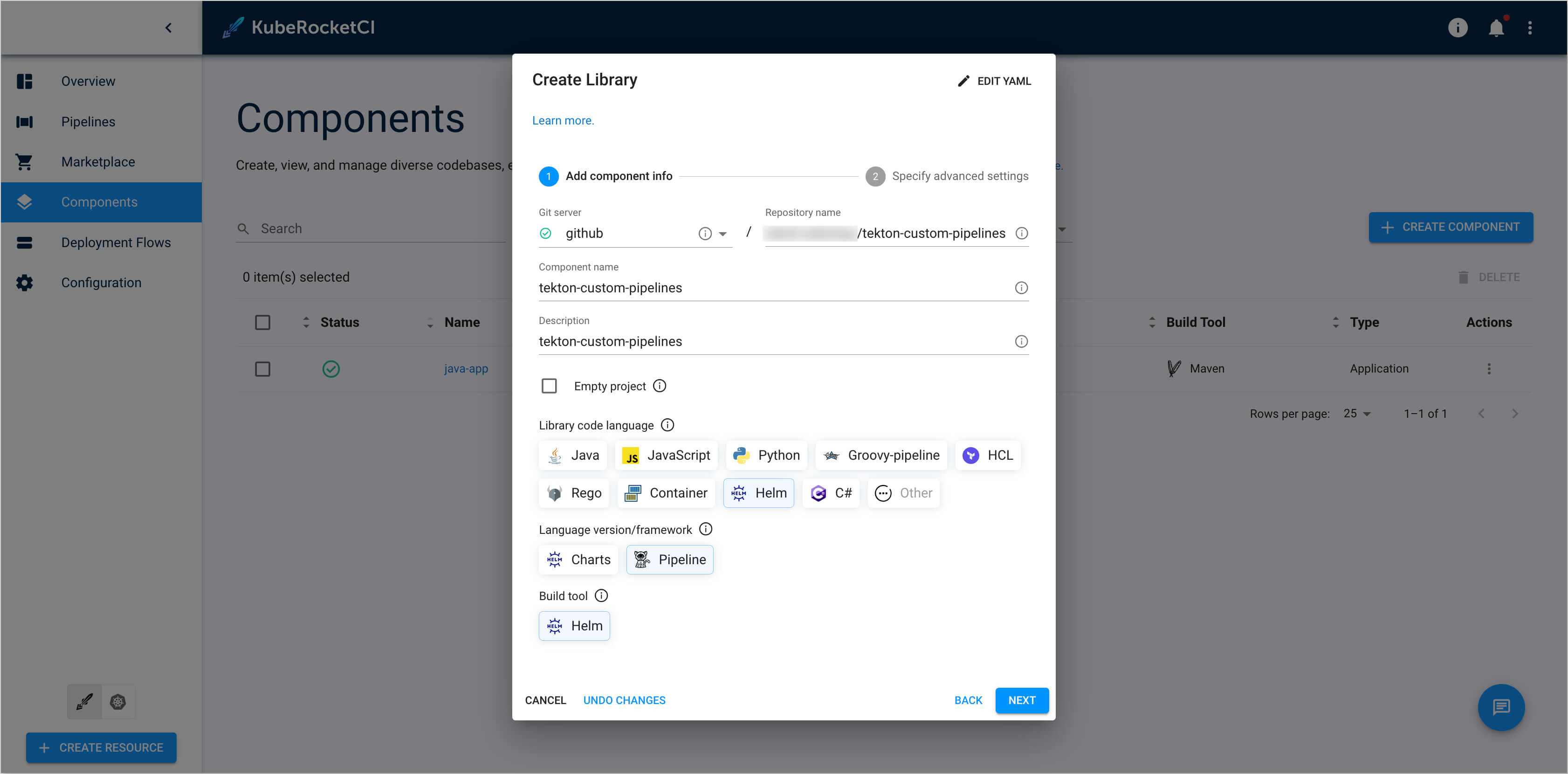
- Repository Name:
-
In the
Specify Advanced Settingssection, you can leave all fields at their default values. Click theCreatebutton to create the Tekton library: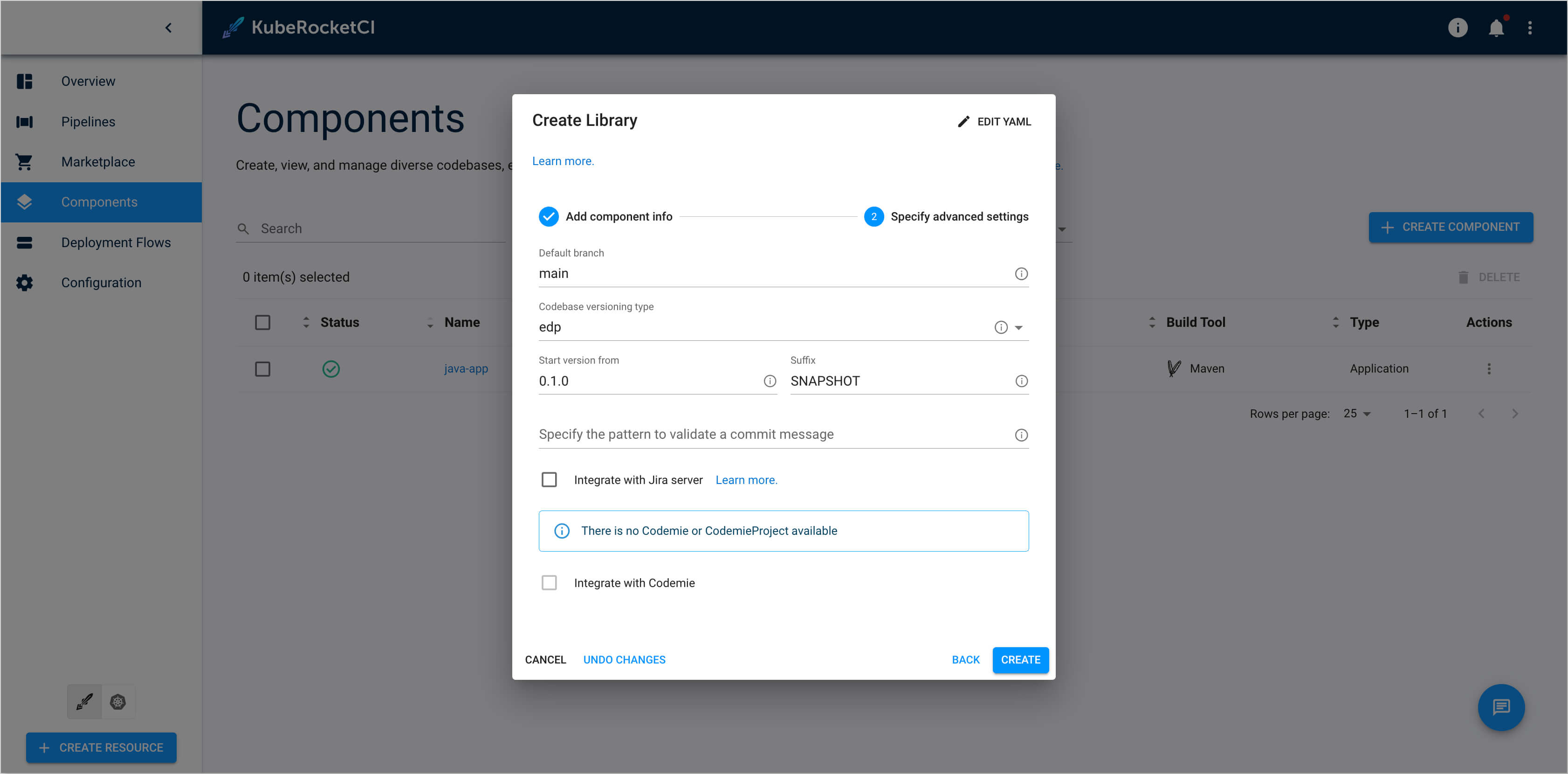
-
Once the library is created, you can start adding custom Tekton tasks, pipelines, and trigger templates to the library.
Defining Custom Tekton Pipelines
After creating the Tekton library, the next step is to define custom Tekton pipelines for build, review or deployment processes based on your project requirements.
To define custom Tekton pipelines, follow these steps:
-
In the KubeRocketCI portal, navigate to the
Componentstab and select the newly createdtekton-custom-pipelineslibrary: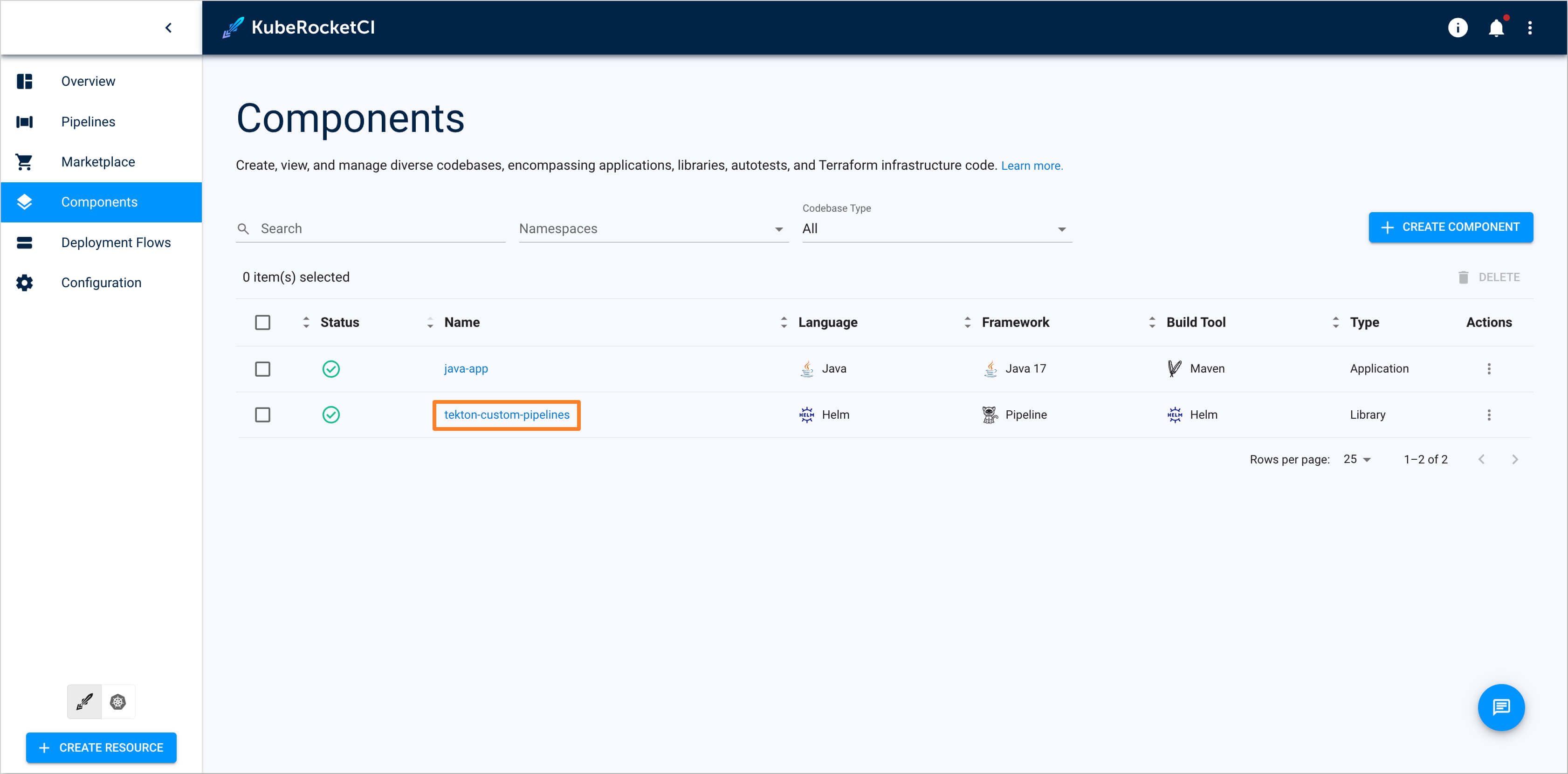
-
In the top-right corner, click the Git button to open the Git repository for the
tekton-custom-pipelineslibrary: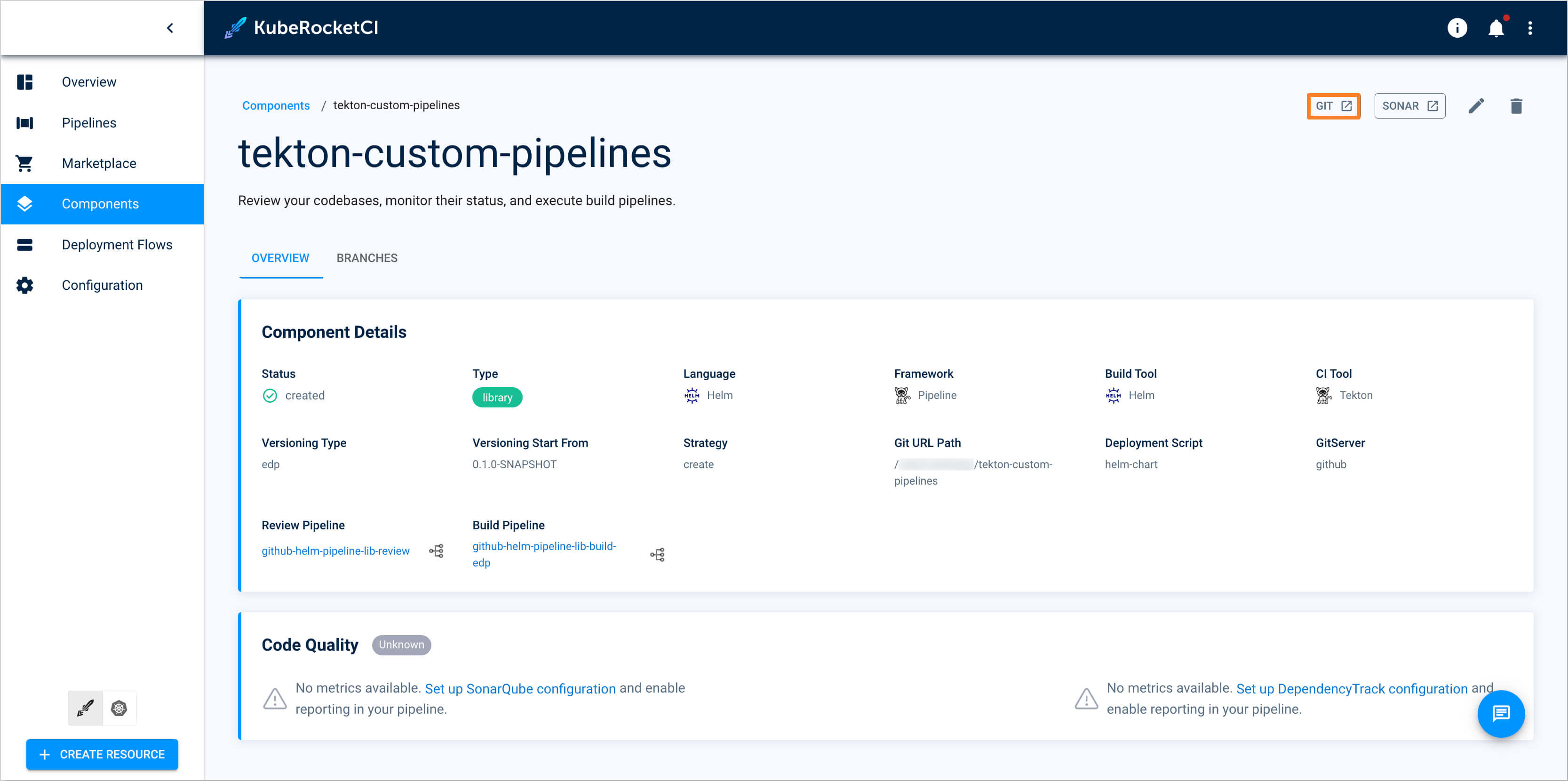
-
Clone the repository to your local machine:
You can use the following command to clone the repository:
git clone <git-repo-url> -
Examine the repository structure.
By default, the repository structure looks as follows:
tekton-custom-pipelines
├── Chart.yaml
├── templates
│ ├── pipelines
│ │ ├── deploy
│ │ │ ├── custom-clean.yaml
│ │ │ └── custom-deploy.yaml
│ │ ├── bitbucket-build-default.yaml
│ │ ├── bitbucket-build-edp.yaml
│ │ ├── bitbucket-build-lib-default.yaml
│ │ ├── bitbucket-build-lib-edp.yaml
│ │ ├── bitbucket-review.yaml
│ │ ├── gerrit-build-default.yaml
│ │ ├── gerrit-build-edp.yaml
│ │ ├── gerrit-build-lib-default.yaml
│ │ ├── gerrit-build-lib-edp.yaml
│ │ ├── gerrit-review.yaml
│ │ ├── github-build-default.yaml
│ │ ├── github-build-edp.yaml
│ │ ├── github-build-lib-default.yaml
│ │ ├── github-build-lib-edp.yaml
│ │ ├── github-review.yaml
│ │ ├── gitlab-build-default.yaml
│ │ ├── gitlab-build-edp.yaml
│ │ ├── gitlab-build-lib-default.yaml
│ │ ├── gitlab-build-lib-edp.yaml
│ │ └── gitlab-review.yaml
│ ├── resources
│ │ └── npm-settings.yaml
│ ├── tasks
│ │ ├── deploy
│ │ │ └── hello-world-deploy.yaml
│ │ └── hello-world.yaml
│ └── triggers
│ ├── custom-clean.yaml
│ └── custom-deploy.yaml
└── values.yaml-
The
templatesdirectory is a main directory that contains templates for custom Tekton resources. This directory is divided into subdirectories for pipelines, tasks, triggers, and resources. -
The
templates/pipelinesdirectory contains Tekton pipeline templates for build and review processes. For each Git server (e.g., GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, or Gerrit), there are specific templates, organized by component and versioning type.-
The appropriate template should be selected based on the configuration of your component. For example:
- If the component is created in GitHub, has the
Applicationcomponent type, and usesedpversioning, you should use thegithub-build-edp.yamltemplate. - If the component is created in Bitbucket, has the
Librarycomponent type, and uses thedefaultversioning, you should use thebitbucket-build-lib-default.yamltemplate.
Here is an example illustrating the naming conventions used in template filenames:
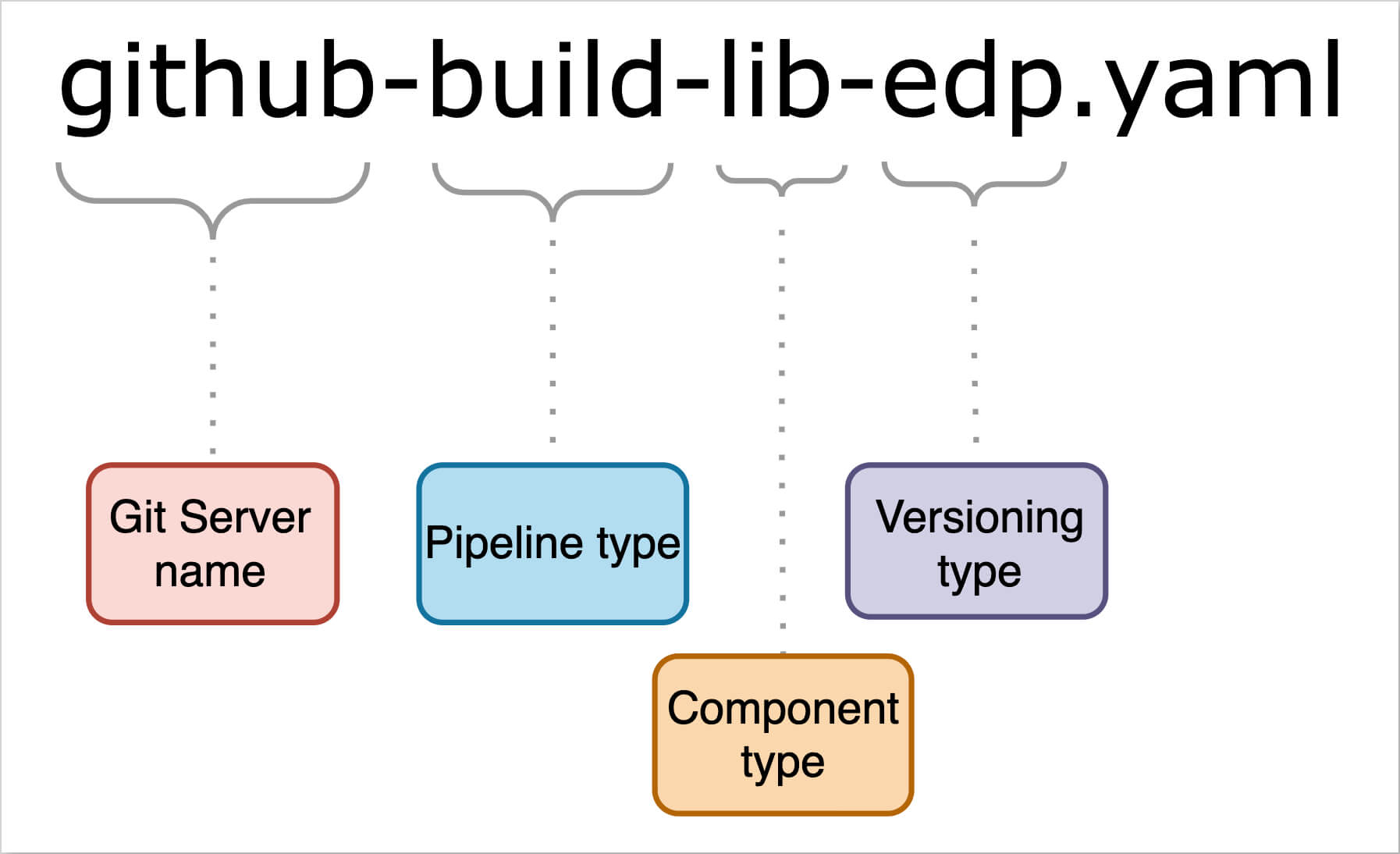
- If the component is created in GitHub, has the
-
-
The
templates/pipelines/deploydirectory contains Tekton pipeline templates for deploy and clean processes. Select the appropriate template based on the deployment process requirements. -
The
templates/tasksdirectory contains Tekton task templates for specific tasks that are part of the build, review, or deployment processes. -
The
templates/triggersdirectory contains Tekton trigger templates for triggering the deployment or clean processes. -
The
templates/resourcesdirectory is intended for various templates, such as config maps and secrets, which can be mounted into custom Tekton tasks as needed.
-
-
Modify the existing pipeline and task templates or create new ones based on your project requirements.
Result: This step will demonstrate an example of creating custom Tekton resources. After completing this step, you will have a custom Tekton task, pipeline, and trigger template.
Usage: The created custom Tekton resources can be used later for components on the KubeRocketCI platform. This flow serves as an example that can be used when creating your own, specific custom Tekton resources for your project's needs
Consider the scenario where a custom task
hello-worldneeds to be created and used in a custom Tekton pipeline. Follow the steps below to achieve this:-
Create a custom Tekton task.
Create a custom Tekton task called
hello-worldto be used in a custom build pipeline. This task should be created in thetemplates/tasksdirectory with the namehello-world.yaml. The task will accept two parameters:BASE_IMAGEandusername. TheBASE_IMAGEparameter specifies the base Docker image to be used for the task, while theusernameparameter is used to personalize the task's output.Here is an example of the
hello-world.yamltask template:apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1beta1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: hello-world
labels:
{{- include "edp-tekton.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
spec:
params:
- name: BASE_IMAGE
type: string
default: "alpine"
description: "The base Docker image to use for the task"
- name: username
type: string
description: "The username to personalize the task's output"
workspaces:
- description: A workspace that contains fetched git repo.
name: source
steps:
- name: hello-world
image: $(params.BASE_IMAGE)
workingDir: $(workspaces.source.path)
script: |
#!/bin/sh
echo "Hello $(params.username), the repository contains the following files:"
ls -al -
Create a Custom Tekton Pipeline.
Define a custom Tekton pipeline that uses the
hello-worldcustom task. Since the application for which this pipeline will be used is located in GitHub, has the component typeApplication, and has the versioning typeedp, use the templategithub-build-edp.yamlin thetemplates/pipelinesdirectory. First, set the parameters in thespec.paramsfield that will be used in the custom task:labels:
app.edp.epam.com/pipelinetype: build
...
spec:
params:
- default: "World"
description: "Example parameter"
name: username
type: string
- default: 'alpine:3.18.9'
name: image-version
type: stringThen, in the
spec.tasksfield, after theget-versiontask, describe the customhello-worldtask. Also, in the subsequentgit-tagtask, specify therunAfter: hello-worldfield to maintain the sequence of execution.Here is an example of part of the
github-build-edp.yamlpipeline template:apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1
kind: Pipeline
metadata:
name: custom-deploy
labels:
app.edp.epam.com/pipelinetype: deploy
spec:
tasks:
...
- name: hello-world
taskRef:
name: hello-world
runAfter:
- get-version
params:
- name: BASE_IMAGE
value: "$(params.image-version)"
- name: username
value: "$(params.username)"
workspaces:
- name: source
workspace: shared-workspace
subPath: source
- name: git-tag
params:
- name: GIT_USER_EMAIL
value: edp-ci@edp.ci-user
- name: GIT_USER_NAME
value: edp-ci
- name: GIT_SCRIPT
value: |
git tag -a "$(tasks.get-version.results.VCS_TAG)" -m "Tag is added automatically by CI user"
git push --tags
runAfter:
- hello-world
taskRef:
kind: Task
name: git-cli
... -
Create a Custom Tekton Trigger Template.
Create a Tekton Trigger Template to invoke the custom
github-build-edp pipeline. Use thecustom-deploy.yamltemplate in thetemplates/triggersdirectory. Modify the.spec.resourcetemplates.spec.pipelineRef.namefield to reference the custom pipeline that uses thehello-worldcustom Tekton task, in this case,custom-deploy.Here is the relevant part of the
custom-deploy.yamltrigger template:apiVersion: triggers.tekton.dev/v1beta1
kind: TriggerTemplate
metadata:
name: custom-deploy
labels:
app.edp.epam.com/pipelinetype: deploy
...
spec:
resourcetemplates:
- apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1beta1
kind: PipelineRun
...
spec:
pipelineRef:
name: custom-deploy
... -
Optional: Specify the
dnsWildCardfield in thevalues.yamlfile.If custom Tekton review pipelines have been created, it is necessary to specify the
dnsWildCardfield in thevalues.yamlfile. This field will be used to form thepipelineUrlvariable, which is utilized in merge and pull requests to navigate to the KubeRocketCI Portal.Here is an example of the
values.yamlfile:dnsWildCard: "example.com"
-
-
Commit and push the changes to the Git repository.
After modifying the pipeline and task templates, commit and push the changes to the Git repository. Use the following commands to commit and push the changes:
git add .
git commit -m "Add custom task and pipeline templates"
git push origin main
Deliver Custom Tekton Pipelines to the Cluster
To deploy custom pipelines to the cluster, you can use Argo CD, which includes a repository with add-ons.
Before proceeding, ensure you have added Add-Ons repository and application according to the Install via Add-Ons page.
To deliver custom Tekton pipelines to the cluster, follow these steps:
-
Clone the private repository with add-ons and make the following changes. In the
clusters/core/apps/values.yamlfile, set therepoUrlandnamespacefields to specify the Git URL of thetekton-custom-pipelinesrepository and the namespace where the KubeRocketCI platform is deployed. Also, set thekuberocketci-pipelines.enabledfield totrueto enable the deployment of thetekton-custom-pipelinesArgo CD Application:kuberocketci-pipelines:
enable: true
namespace: <krci-namespace>
repoUrl: ssh://git@github.com:22/<account-name>/tekton-custom-pipelines.git -
Commit and push the changes to the repository.
After making the necessary changes, commit and push the changes to the repository. Use the following commands to commit and push the changes:
git add .
git commit -m "Enable custom Tekton pipelines deployment"
git push origin main -
After pushing the changes, access Argo CD, navigate to the Application that corresponds to the repository with the add-ons, and initiate the
Syncprocess. This will apply thetekton-custom-pipelinesHelm Chart to the cluster within the specified namespace.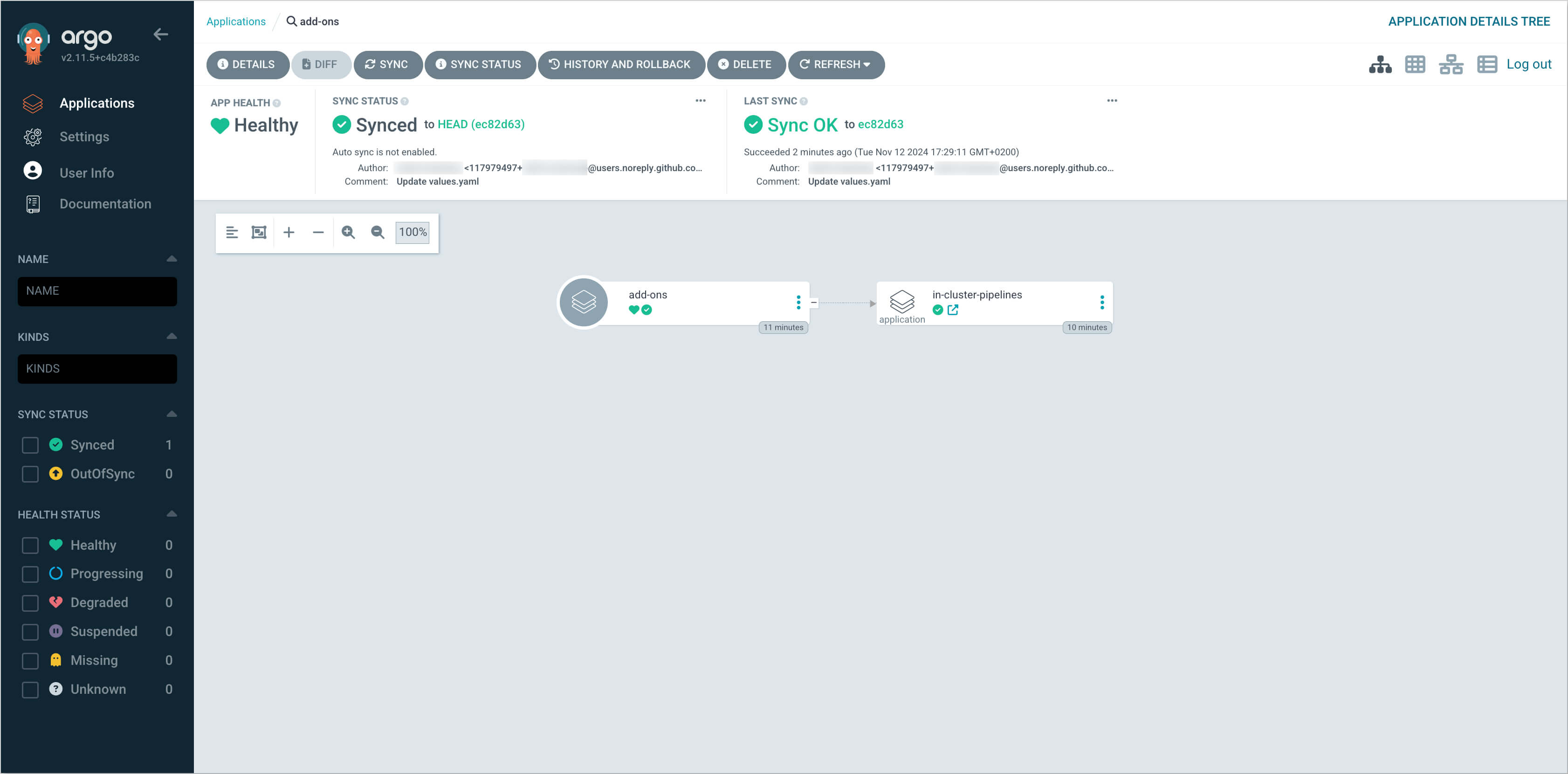
Replace Existing Pipelines for Components With Custom Pipelines
This section demonstrates how to replace existing build, review, deploy, and clean pipelines with custom pipelines in KubeRocketCI. Two cases are covered: replacing build and review pipelines for a created component, and replacing deploy and clean pipelines for an existing deployment flow.
-
To replace existing review or build pipelines for a component with custom pipelines, follow these steps:
-
Open the KubeRocketCI portal. Navigate to the Components tab and select the component for which you want to replace the build or review pipeline:
-
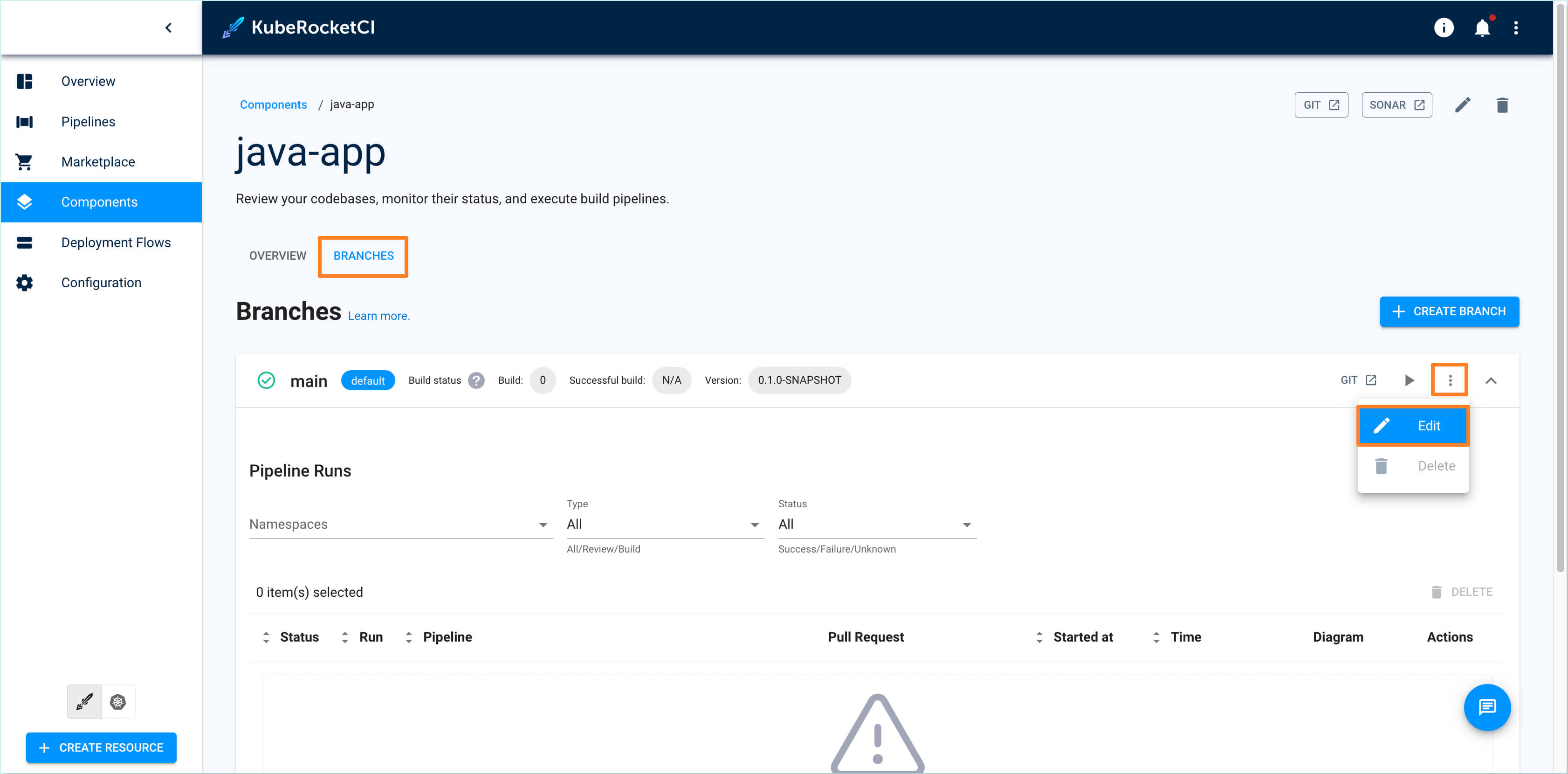
In the Branches tab, select the branch for which you want to replace the pipeline. Click the three dots (⋮) menu and click Edit:
-
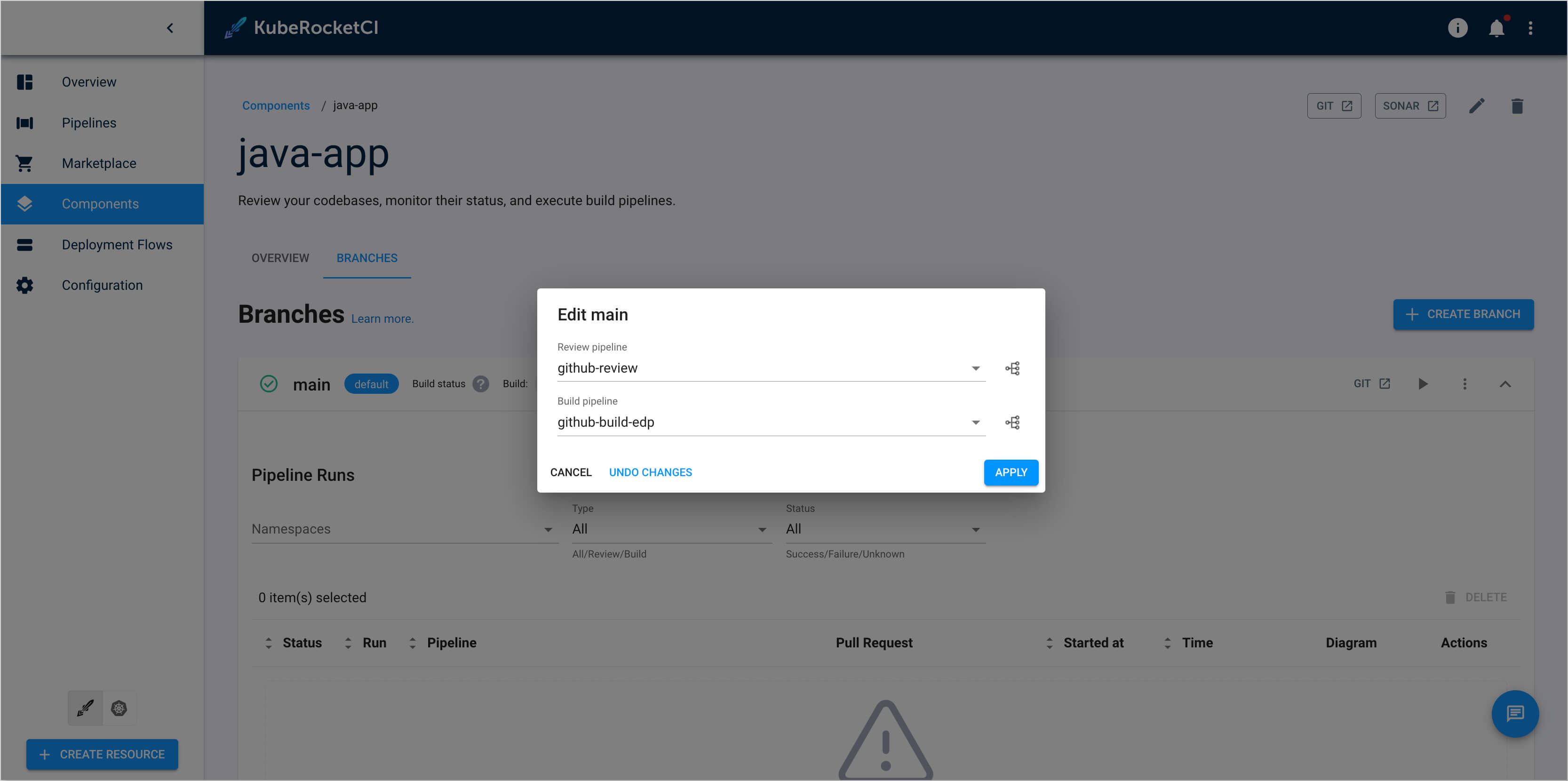
In the Edit branch dialog, select the required build or review pipeline from the dropdown list:
-
-
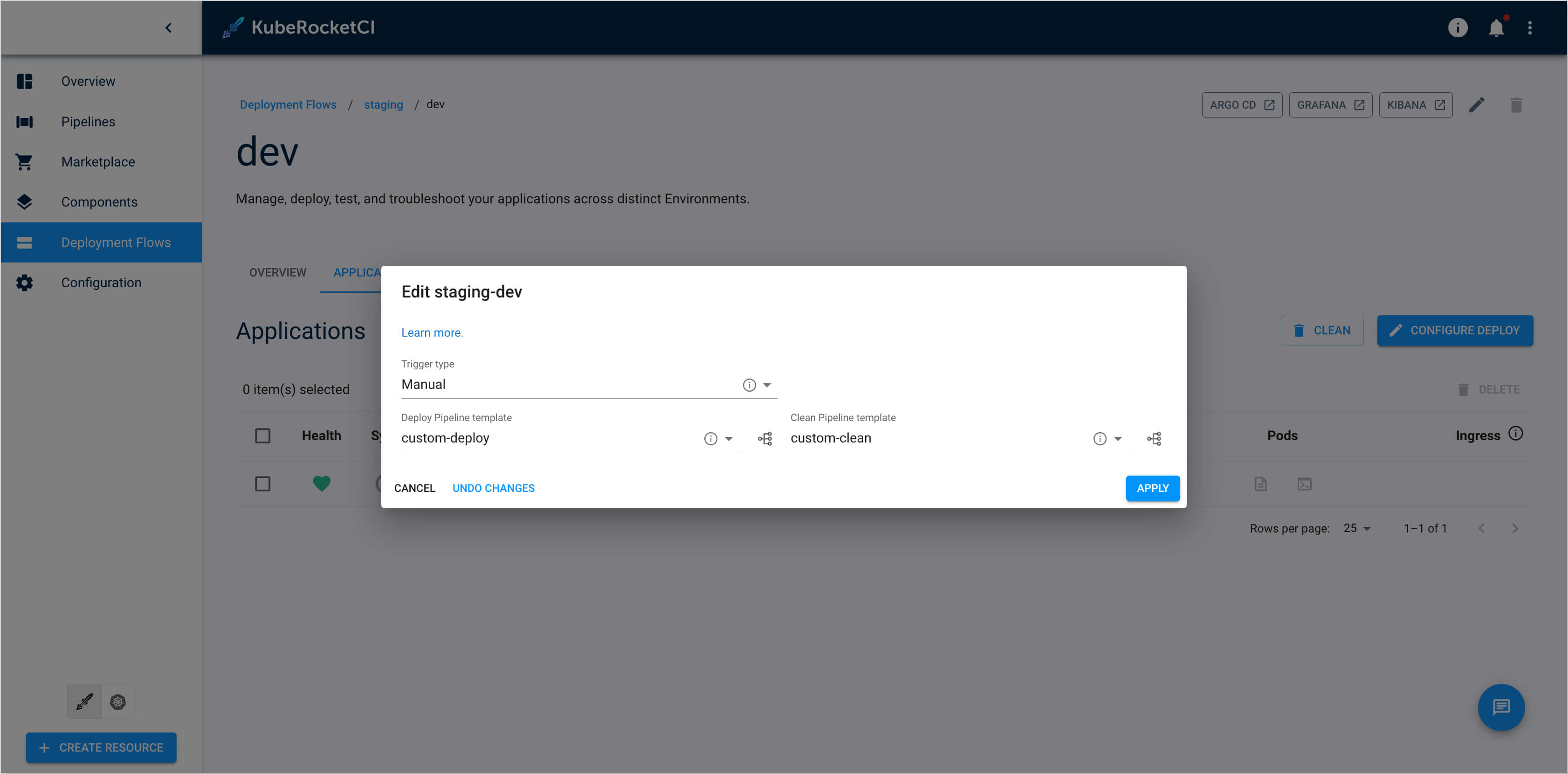
To replace existing deploy or clean pipelines for a deployment flow with custom pipelines, follow these steps:
-
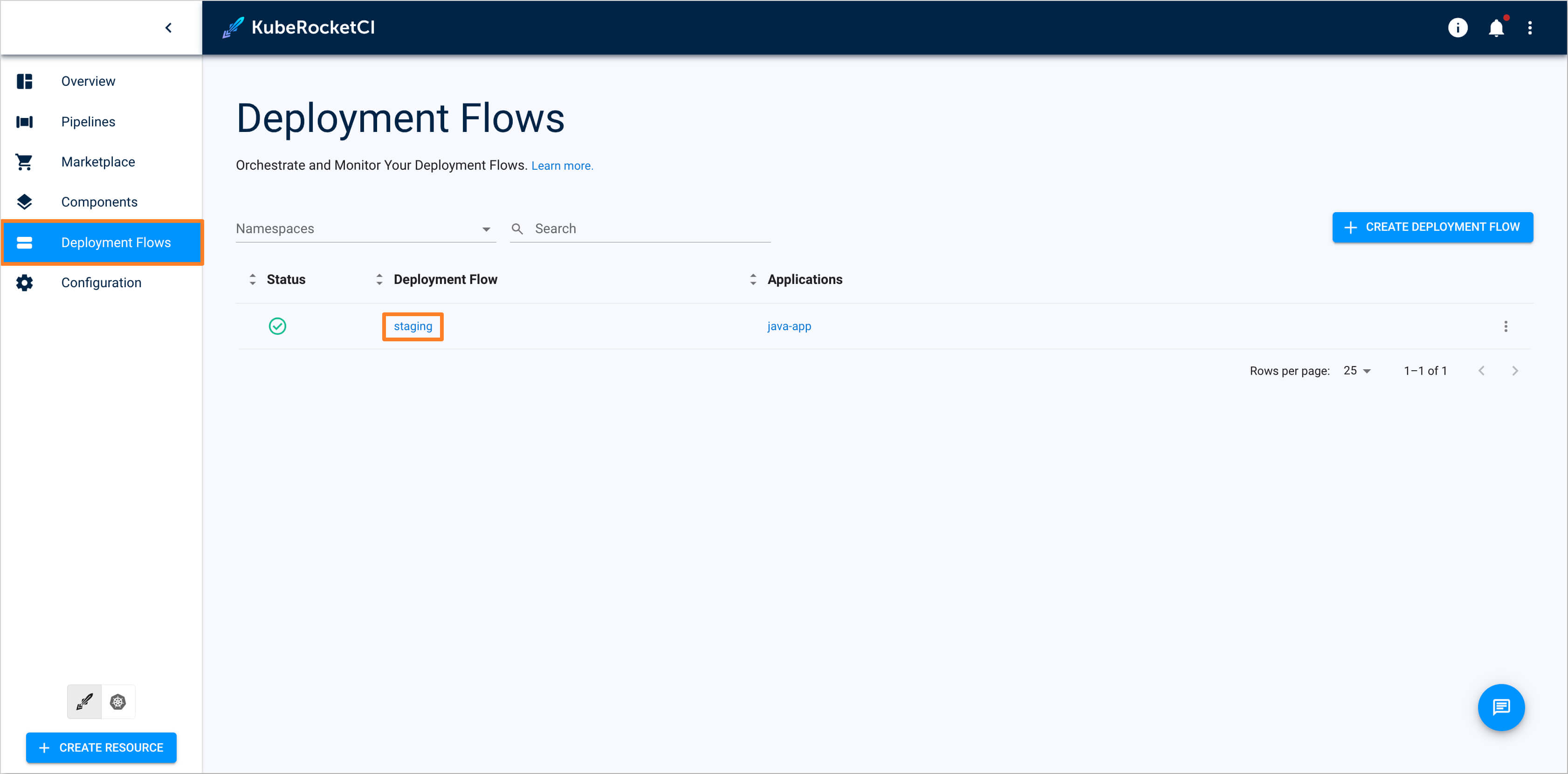
Open the KubeRocketCI portal. Navigate to the Deployment Flows tab and select the deployment flow for which you want to replace the deploy or clean pipeline:
-
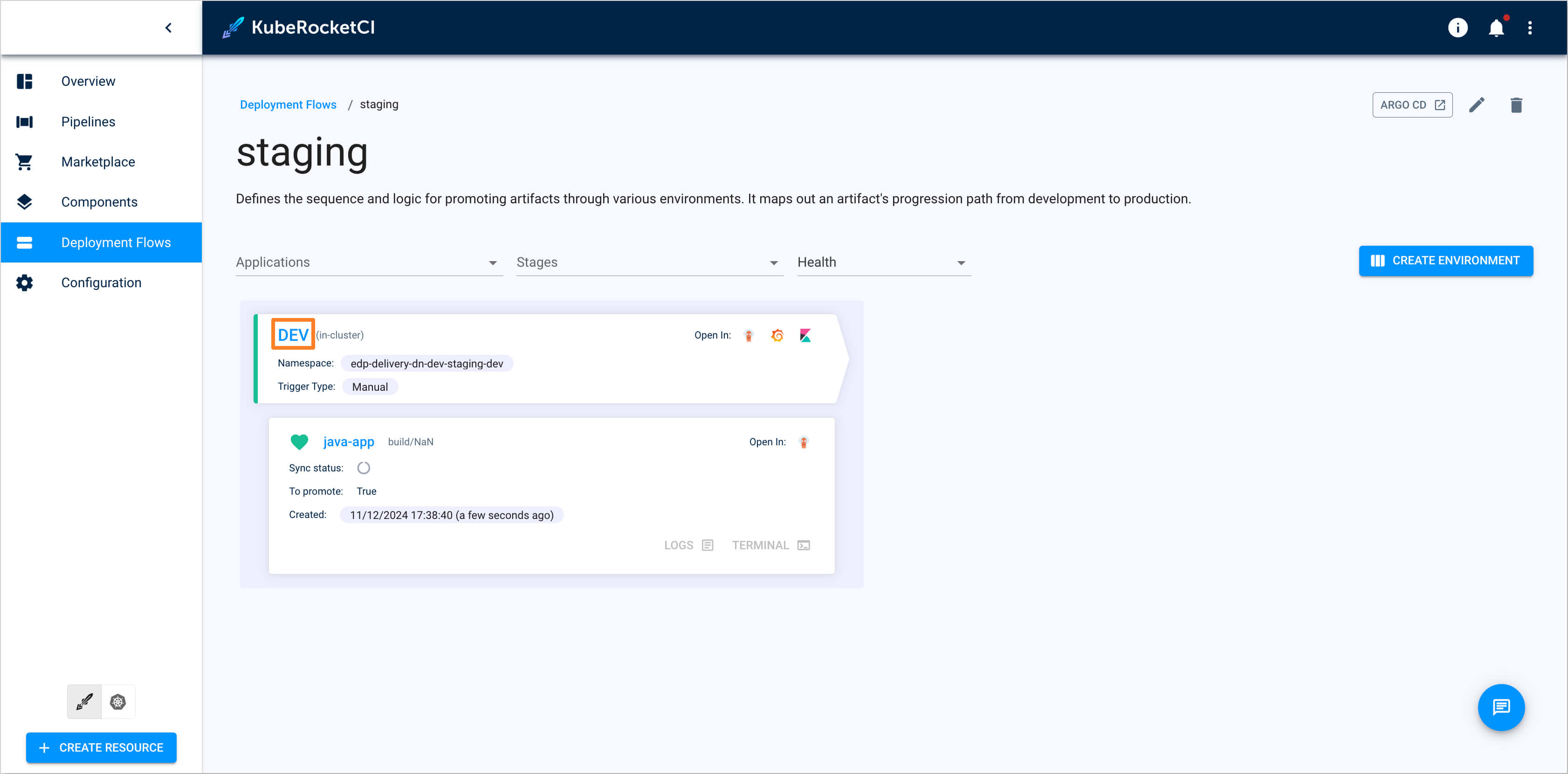
Choose the required Environment:
-
In the Edit Environment dialog, select the required deploy or clean pipeline from the dropdown list:
-